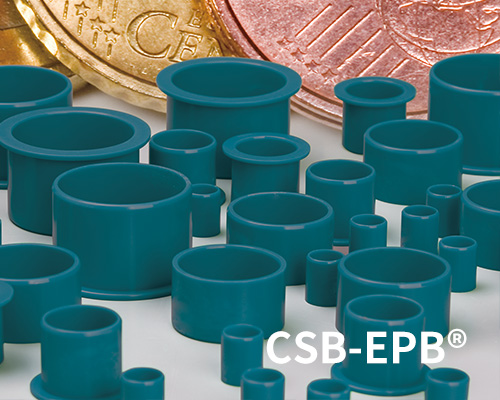


● The combination of middle to low load and low speed application requirement. It is a material without PTFE embedded for the low cost and big quantity demanding
● Continuous working temperature: -40℃/+80℃
● Very common; suitable for most average and low load
● Maintenance-free dry operation
● Light wear against different shaft materials
● Low friction
Material properties | Standard | Unit | CSB-EPB2D |
General properties | |||
Color | - | - | Green |
Density | ISO1183 | g/cm3 | 1.40 |
Max. moisture absorption, 50%RH | ISO62 | % | 0.3 |
Max. water absorption | ISO62 | % | 1.2 |
Coefficient of sliding friction(steel) | ITS025 | µ | 0.05-0.25 |
Max. PV value | ITS026 | N/mm2×m/s | 0.25 |
Mechanical properties | |||
Flexural modulus | ISO178 | MPa | 2000 |
Flexural strength | ISO178 | MPa | 65 |
Max. static load | ITS027 | MPa | 30 |
Max. dynamic load | ITS028 | MPa | 13 |
Shore hardness | ISO868 | D | 75 |
Physical and thermal properties | |||
Long-term application temperature | ITS029 | ℃ | +80 |
Short-term application temperature | ITS029 | ℃ | +120 |
Lowest application temperature | ITS029 | ℃ | -40 |
Thermal conductivity | ISO22007 | W/m/K | 0.25 |
Coefficient of thermal expansion | ISO11359 | K-1×10-5 | 11 |
Flammability | UL94 | Class | HB |
Electrical properties | |||
Volume resistance | IEC60093 | Ω·cm | >1013 |
Surface resistance | IEC60093 | Ω | >1012 |
*ITS: CSB company's internal test standards. **Test temperatures are 23℃ unless otherwise stated.

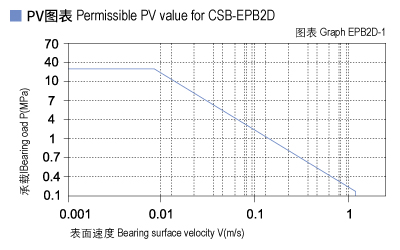
The max PV value of the CSB-EPB2D plastic bearings is 0.25N/mm2×m/s which determines the load capacity of bearing is inversely proportional to the speed. Please refer to the chart for more detailed information (Graph EPB2D-1).
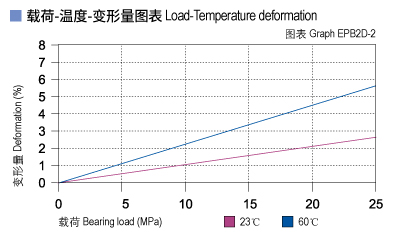
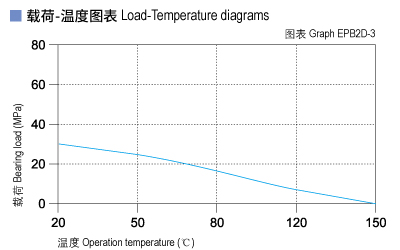
CSB-EPB2D allows the Max static load of 30Mpa, The max compressive deformation rate under the max load is listed in Graph EPB2D-2, The actual load capacity of bearing is slightly less than 30Mpa, The bearing load is variable against the speed and temperature, Fast speed (Vmax: 1.2m/s) results into higher temperature (Tmax: 80℃) which decreases the load capacity of the bearing. Please refer to the Graph EPB2D-3 for such variation.
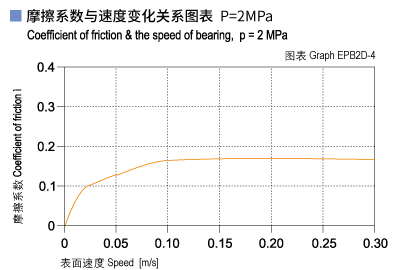
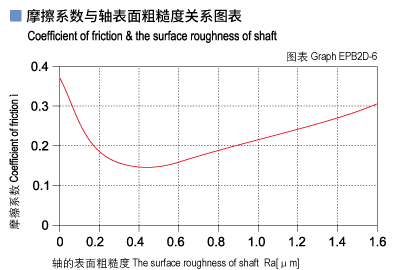
Graph EPB2D-4 shows that the friction factor of CSB-EPB2D is initially increased along with the operation speed increasing when the loading is stable but when the speed reaches over 0.25m/s, it is decreased along with the operation speed increasing. Graph EPB2D-5 shows that the friction factor of CSB-EPB2D is decreasing along with the loading increasing when the operation speed is stable. Graph EPB2D-6 shows the friction factor of CSB-EPB2D is sensitive to the shaft roughness. The best shaft roughness for this material is Ra0.3~0.6.
| CSB-EPB2D | Dry | Grease | Oil | Water |
| Friction coef. μ | 0.05~0.25 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.04 |

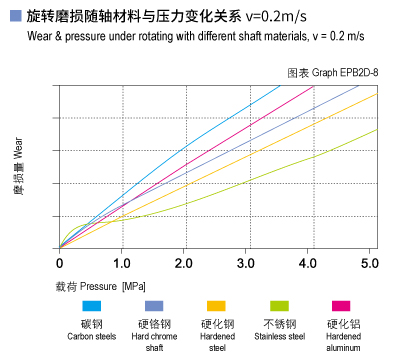
Graph EPB2D-7 and Graph EPB2D-8 shows that the hardened chrome steel shaft is good for CSB-EPB2D bearings under lower loading and stainless steel shaft is better when the loading is over 1.0Mpa. Hardened steel shaft is recommended in rotation operation but hardened chrome steel shaft is recommended in oscillation operation.

CSB-EPB2D is good at chemical resistance against mild base, weak acidic medium and various kinds of lubricants.
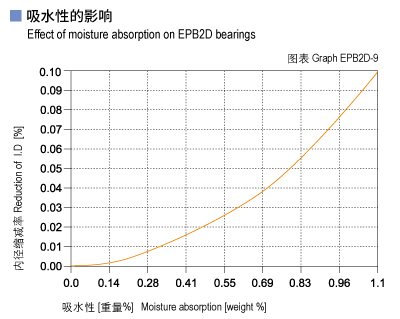
The moisture absorption of CSB-EPB2D plastic bearings is 0.3% in standard atmosphere. The max. water absorption is 1.2% in water. These values are so low that design changes due to absorption are only necessary in extreme applications.
The color of CSB-EPB2D will become lighter when it is exposed into the UV ray. The hardness, Compressive strength and wear resistance of the material is also stable under such condition.
CSB-EPB2D Tolerances after pressfit
Diameter [mm] | CSB-EPB2D E10 [mm] | Housing H7 [mm] | Shaft h9 [mm] |
>0~3 | +0.014~+0.054 | 0~+0.010 | 0~-0.025 |
>3~6 | +0.020~+0.068 | 0~+0.012 | 0~-0.030 |
>6~10 | +0.025~+0.083 | 0~+0.015 | 0~-0.036 |
>10~18 | +0.032~+0.102 | 0~+0.018 | 0~-0.043 |
>18~30 | +0.040~+0.124 | 0~+0.021 | 0~-0.052 |
>30~50 | +0.050~+0.150 | 0~+0.025 | 0~-0.062 |
>50~80 | +0.060~+0.180 | 0~+0.030 | 0~-0.074 |
>80~120 | +0.072~+0.212 | 0~+0.035 | 0~-0.087 |
>120~180 | +0.085~+0.245 | 0~+0.040 | 0~-0.100 |
▊CSB-EPB® Plastic Bearings Finder[V2.1] is based on the analysis and calculation of a large number of test data in CSB® laboratory. You can calculations material data by entering parameters such as bearing load, speed, and temperature, and finally output material adaptation data.
▊Because the system calculate and analyze based on lab data, it can't exactly meet the ractual use requirements absolutly. The system data verification has certain limitations; CSB® recommends that the bearing must be tested again to verify whether it meets the actual use requirements.
▊CSB-EPB® Plastic Bearings Finder output data information is only for design reference, and can not be used as the final standard for determining the bearing material conformity, If you have any questions, please contact CSB® sales engineers.
▊DURAPLAS® Semi-finished Products Finder[V2.0] is based on the analysis and calculation of a large number of test data in CSB® laboratory. You can calculations material data by entering parameters such as bearing load, speed, and temperature, and finally output material adaptation data.
▊Because the system calculate and analyze based on lab data, it can't exactly meet the ractual use requirements absolutly. The system data verification has certain limitations; CSB® recommends that the products must be tested again to verify whether it meets the actual use requirements.
▊DURAPLAS® Semi-finished Products Finder output data information is only for design reference, and can not be used as the final standard for determining the bearing material conformity, If you have any questions, please contact CSB® sales engineers.
| Medium | EPB2D bearings resistance |
| Alcohol | Resistant |
| Hydrocarbons | Resistant |
| Greases. oils | Resistant |
| Fuels | Resistant |
| Diluted acids | Conditionally resistant |
| Strong acids | Not resistant |
| Diluted alkalis | Resistant |
| Strong alkalis | Conditionally resistant |
Please select bearing material and medium...
▊CSB® bearing material chemical resistance data is a comparison test result of the CSB chemistry laboratory using laboratory specimens or similar chemicals at room temperature 23 ℃, without considering the impact of other temperatures and chemical medium mixtures on the chemical resistance of CSB® bearing materials ; Therefore, this data can only act as a reference. CSB® recommends that the chemical resistance of actual parts should be tested under application conditions and verify the suitability of the bearings.
This material is developed against the requirement of wear resistance and economic cost for cost effective and big quantity comsuming applications. Continuous working temperature: -40℃/+80℃. Suitable for most...
moreOptimized for middle load applications. It is suitable for low frequency motion and low cost requirement. Continuous working temperature: -40℃/+100℃. High load capacity. Good economic ratio. Dry operation and...
more